Springboot注解汇总
目录
Controller请求相关
1.1 @requestBody
1.2 @RequestParam
1.3 @Validated
1.4 @PathVariable
1.5 @Constraint
Service服务类相关
2.1 @Scheduled
2.2 @Async
2.3 事务管理
2.4 @ConfigurationProperties
配置类
3.1 @ControllerAdvice
第三方注入Bean
3.1 @Bean
3.2 @Configuration
3.3 @Qualifier
3.4 @Scope
启动类相关
5.1 @PropertySource
5.2 @ImportResource
参考/来源:
Controller请求相关
@requestBody参数绑定
请求体的Content-Type必须为application/json格式的数据
一般运用在POST请求中,最好后端接口带上此注解。通过@requestBody可以将POST请求体中的JSON字符串绑定到相应的bean上,当然,也可以将其分别绑定到对应的字符串上。
$.ajax({
url:"/login",
type:"POST",
data:'{"userName":"admin","pwd","admin123"}',
content-type:"application/json charset=utf-8",
success:function(data){
alert("request success ! ");
}
});java@requestMapping("/login") public void login(@requestBody User){ System.out.println(userName+" :"+pwd); }
@RequestParam参数说明
如果在方法中的参数增加了该注解,说明请求的url该带有该参数,否则不能执行该方法。如果在方法中的参数没有增加该注解,说明请求的url无需带有该参数,也能继续执行该方法。
也可以通过此注解进行参数的别名设置
@RequestParam(defaultValue="0") //可设置默认值(仅当传入参数为空时)。
@RequestParam(value="id") //可接受传入参数为id的值,覆盖该注解注释的字段。
@RequestParam(name="name",defaultValue = "李四") String u_name //如果传入字段”name”为空,默认u_name的值为”李四”。若传入”name”不为空,默认u_name值为传入值。
/** * 自定义方法参数名-当请求参数名与方法参数名不一致时
* @param u_name 用户名
* @param u_pwd 密码
* @return*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/addByDifName", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"})
@ResponseBodypublicString addUserByDifName(@RequestParam("name") String u_name, @RequestParam("pwd")String u_pwd){
logger.debug("name:" + u_name + ",pwd:" + u_pwd);
return"name:" + u_name + ",pwd:" + u_pwd;
}@Validated字段校验
简述
@Validation是一套帮助我们继续对传输的参数进行数据校验的注解,通过配置Validation可以很轻松的完成对数据的约束。
@Validated作用在类、方法和参数上
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Validated {
Class<?>[] value() default {};
}校验错误时的状态码
返回的响应码推荐使用400 bad request.
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
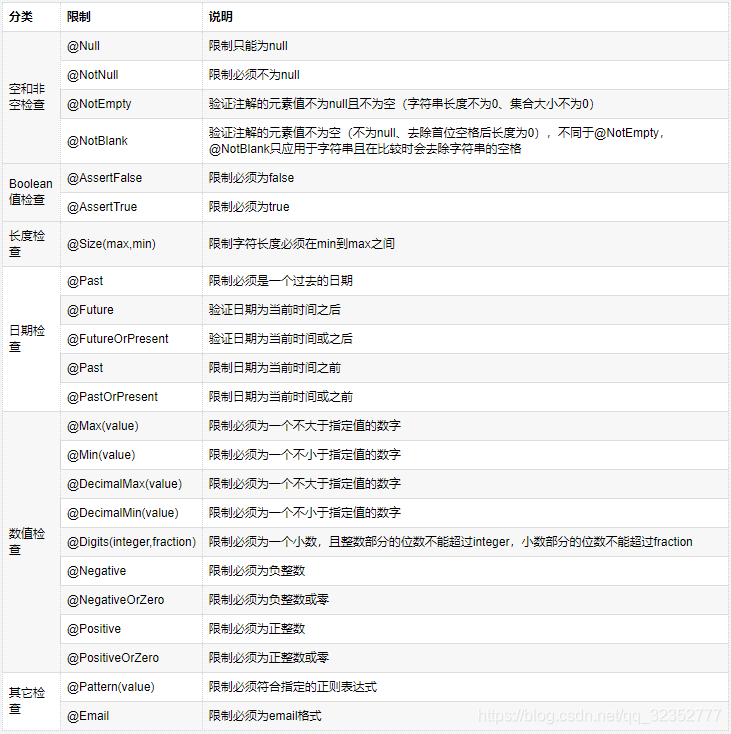
</dependency>校验注解
全局异常处理类
说明:若不做异常处理,@Validated注解的默认异常消息如下(示例):
2020-09-05 21:48:38.106 WARN 9796 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] .w.s.m.s.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver : Resolved [org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException: Validation failed for argument [0] in public java.lang.String com.example.validateddemo.controller.DemoController.validatedDemo1(com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.UseDto): [Field error in object 'useDto' on field 'username': rejected value [null]; codes [NotBlank.useDto.username,NotBlank.username,NotBlank.java.lang.String,NotBlank]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [useDto.username,username]; arguments []; default message [username]]; default message [用户名不能为空!]] ]
因此我们在这里做了一个全局的异常处理类,用于处理参数校验失败后抛出的异常,同时进行日志输出。
package com.example.validateddemo.handler;
import com.example.validateddemo.base.Result;
import com.example.validateddemo.enums.ResultEnum;
import com.example.validateddemo.utils.ResultUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5
*/
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class ValidatedExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理@Validated参数校验失败异常
* @param exception 异常类
* @return 响应
*/
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException exception){
BindingResult result = exception.getBindingResult();
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
if (result.hasErrors()) {
List<ObjectError> errors = result.getAllErrors();
if (errors != null) {
errors.forEach(p -> {
FieldError fieldError = (FieldError) p;
log.warn("Bad Request Parameters: dto entity [{}],field [{}],message [{}]",fieldError.getObjectName(), fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
stringBuilder.append(fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
});
}
}
return ResultUtil.validatedException(stringBuilder.toString());
}基础参数校验
实体类
package com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat; import javax.validation.constraints.*; /** * 用户实体 * 数据传输对象 * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @Data public class User1Dto { /** * 用户名 */ @NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空!") private String username; /** * 性别 */ @NotBlank(message = "性别不能为空!") private String gender; /** * 年龄 */ @Min(value = 1, message = "年龄有误!") @Max(value = 120, message = "年龄有误!") private int age; /** * 地址 */ @NotBlank(message = "地址不能为空!") private String address; /** * 邮箱 */ @Email(message = "邮箱有误!") private String email; /** * 手机号码 */ @Pattern(regexp = "^(13[0-9]|14[579]|15[0-3,5-9]|16[6]|17[0135678]|18[0-9]|19[89])\\d{8}$",message = "手机号码有误!") private String mobile; }控制类
package com.example.validateddemo.controller; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.Use1Dto; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class Demo1Controller { @PostMapping("/insert") public String validatedDemo1(@Validated @RequestBody Use1Dto use1Dto){ System.out.println(use1Dto); return "success"; } }
嵌套参数校验
验证实体中的其他需要被验证的对象集合或其他对象.
注意这里的@Valid注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Valid {
}@Valid:没有分组的功能。
@Valid:可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(字段)上
@Validated:提供了一个分组功能,可以在入参验证时,根据不同的分组采用不同的验证机制
@Validated:可以用在类型、方法和方法参数上。但是不能用在成员属性(字段)上
两者是否能用于成员属性(字段)上直接影响能否提供嵌套验证的功能
实体类
package com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto; import lombok.Data; import javax.validation.Valid; import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import java.util.List; /** * 队伍实体 * 数据传输对象 * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @Data public class Team1Dto { /** * 队伍名称 */ @NotBlank(message = "队伍名称不能为空!") private String name; /** * 队伍人员 */ @NotNull(message = "队伍人员不能为空!") @Valid private List<User1Dto> userList; /** * 队伍负责人 */ @NotNull(message = "队伍负责人不能为空!") @Valid private User1Dto user; }控制类
package com.example.validateddemo.controller; import com.example.validateddemo.base.Result; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.Team1Dto; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.Use1Dto; import com.example.validateddemo.utils.ResultUtil; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class Demo1Controller { @PostMapping("/insert") public Result validatedDemo1(@Validated @RequestBody Use1Dto use1Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(use1Dto); } @PostMapping("/insert2") public Result validatedDemo2(@Validated @RequestBody Team1Dto team1Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(team1Dto); } }
分组参数验证
将不同的校验规则分给不同的组,在使用时,指定不同的校验规则
- 接口类
package com.example.validateddemo.interfaces;
/**
* 校验分组1
* @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5
*/
public interface Group1 {
}package com.example.validateddemo.interfaces;
/**
* 校验分组2
* @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5
*/
public interface Group2 {
}实体类
package com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto; import com.example.validateddemo.interfaces.Group1; import com.example.validateddemo.interfaces.Group2; import lombok.Data; import javax.validation.constraints.*; /** * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @Data public class User2Dto { /** * 用户名 */ @NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空!", groups = {Group1.class}) private String username; /** * 性别 */ @NotBlank(message = "性别不能为空!") private String gender; /** * 年龄 */ @Min(value = 1, message = "年龄有误!", groups = {Group1.class}) @Max(value = 120, message = "年龄有误!", groups = {Group2.class}) private int age; /** * 地址 */ @NotBlank(message = "地址不能为空!") private String address; /** * 邮箱 */ @Email(message = "邮箱有误!", groups = {Group2.class}) private String email; /** * 手机号码 */ @Pattern(regexp = "^(13[0-9]|14[579]|15[0-3,5-9]|16[6]|17[0135678]|18[0-9]|19[89])\\d{8}$",message = "手机号码有误!", groups = {Group2.class}) private String mobile; }控制类
package com.example.validateddemo.controller; import com.example.validateddemo.base.Result; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.Team1Dto; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.User1Dto; import com.example.validateddemo.entity.dto.User2Dto; import com.example.validateddemo.interfaces.Group1; import com.example.validateddemo.interfaces.Group2; import com.example.validateddemo.utils.ResultUtil; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @author He Changjie on 2020/9/5 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/api/v1") public class Demo1Controller { @PostMapping("/insert") public Result validatedDemo1(@Validated @RequestBody User1Dto user1Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(user1Dto); } @PostMapping("/insert2") public Result validatedDemo2(@Validated @RequestBody Team1Dto team1Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(team1Dto); } @PostMapping("/insert3") public Result validatedDemo3(@Validated @RequestBody User2Dto user2Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(user2Dto); } @PostMapping("/insert4") public Result validatedDemo4(@Validated(Group1.class) @RequestBody User2Dto user2Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(user2Dto); } @PostMapping("/insert5") public Result validatedDemo5(@Validated(Group2.class) @RequestBody User2Dto user2Dto){ return ResultUtil.success(user2Dto); } }
@PathVariable获取占位符值
语法
@PathVariable("xxx")
通过 @PathVariable 可以将URL中占位符参数{xxx}绑定到处理器类的方法形参中@PathVariable(“xxx“)@RequestMapping(value=”user/{id}/{name}”)
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/hello/show5/1/james示例
package com.day01springmvc.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; /** * @ Author :ShaoWei Sun. * @ Date :Created in 20:58 2018/11/16 */ @Controller @RequestMapping("hello") public class HelloController2 { /** *3、占位符映射 * 语法:@RequestMapping(value=”user/{userId}/{userName}”) * 请求路径:http://localhost:8080/hello/show5/1/james * @param ids * @param names * @return */ @RequestMapping("show5/{id}/{name}") public ModelAndView test5(@PathVariable("id") Long ids ,@PathVariable("name") String names){ ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); mv.addObject("msg","占位符映射:id:"+ids+";name:"+names); mv.setViewName("hello2"); return mv; } }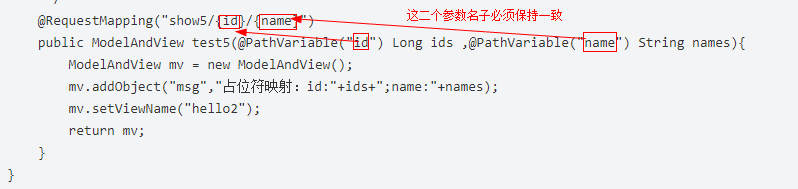
@Constraint自定义字段校验
注解
@Null 被注释的元素必须为 null
@NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为 null
@AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为 true
@AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为 false
@Min(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@Max(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@DecimalMin(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@Size(max, min) 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
@Digits (integer, fraction) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
@Past 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期
@Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期
@Pattern(value) 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
示例
需求:现在有的列表查询,根据查询条件进行查询,当然这些查询条件可以为null,如果存在值,就必须进行验证。这里就对长度就行验证,不为nul的时候 输入字符不能为空串,且长度必须大于等于1且小于等于10
自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //代表处理逻辑是MyConstraintValidator类 @Constraint(validatedBy = MyConstraintValidator.class) public @interface MyConstraint { String message() default "参数校验不通过,请重新输入";; long min(); long max(); Class<?>[] groups() default {}; Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {}; }校验处理类
public class MyConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<MyConstraint, Object> { private long max = 1; private long min = 1; @Override public void initialize(MyConstraint constraintAnnotation) { max = constraintAnnotation.max(); min = constraintAnnotation.min(); System.out.println("my validator init"); } @Override public boolean isValid(Object o, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) { if(o == null){ return true; } if(o.toString().trim().length()>=min && o.toString().trim().length()<=max){ return true; } return false; } }实体类
@Data public class User { @MyConstraint( min = 1, max =10 ) private String name; private String address; }全局异常处理
@RestControllerAdvice @Slf4j public class KevinExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public String handleException(Exception e) { log.error(e.getMessage(), e); if (e instanceof BindException) { BindException ex = (BindException) e; List<ObjectError> allErrors = ex.getAllErrors(); ObjectError error = allErrors.get(0); String defaultMessage = error.getDefaultMessage(); return defaultMessage; } else { return "error"; } } }控制类
@RestController public class Hello { @RequestMapping(value = "hello") public User hello(@Valid User user){ return user; } }
Service服务类相关
@Scheduled创建定时任务
- 在Spring Boot的主类中加入@EnableScheduling注解,启用定时任务的配置。
- 设置时间方式:
固定时间频率运行方法。@Scheduled(fixedRate=30000)
延迟指定的时间运行方法。@Scheduled(fixedDelay=30000)
按照 cron 表达式定义的时间方式运行方法。@Scheduled(cron=”0 0 * * * *”)
@Component
public class ScheduledTasks {
private static final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)
public void reportCurrentTime() {
System.out.println("现在时间:" + dateFormat.format(new Date()));
}
}@Async实现异步调用
启动加上@EnableAsync,需要执行异步方法上加入 @Async
事务管理
@Transactional
springboot默认集成事物,只主要在方法上加上@Transactional即可。
分布式事务管理
使用springboot+jta+atomikos 分布式事物管理。
maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos</artifactId>
</dependency>@ConfigurationProperties全局配置参数
如果我们需要取 N 个配置项,通过 @Value(“${name}”) 的方式去配置项需要一个一个去取,这就显得有点 low 了。我们可以使用 @ConfigurationProperties 。标有 @ConfigurationProperties 的类的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置项进行绑定。(默认从全局配置文件中获取配置值),绑定之后我们就可以通过这个类去访问全局配置文件中的属性值了。
(1) 在主配置文件中添加如下配置
person:
name: kundy
age: 13
sex: male(2)创建配置类,其中setter、getter 方法是实际开发中这个是必须的,否则无法成功注入。另外,@Component 这个注解也还是需要添加的。
@Component
@Setter
@Getter
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
public class Person{
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
}这里 @ConfigurationProperties 有一个 prefix 参数,主要是用来指定该配置项在配置文件中的前缀。
配置类
@ControllerAdvice全局异常处理
SpringBoot中,@ControllerAdvice 即可开启全局异常处理,使用该注解表示开启了全局异常的捕获,我们只需在自定义一个方法使用@ExceptionHandler注解然后定义捕获异常的类型即可对这些捕获的异常进行统一的处理。
自定义全局异常
/** * @description: 自定义异常处理 * @author: DT * @date: 2021/4/19 21:17 * @version: v1.0 */ @ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(value =Exception.class) @ResponseBody public String exceptionHandler(Exception e){ System.out.println("全局异常捕获>>>:"+e); return "全局异常捕获,错误原因>>>"+e.getMessage(); } }手动抛出异常测试
@GetMapping("/getById/{userId}") public CommonResult<User> getById(@PathVariable Integer userId){ // 手动抛出异常 int a = 10/0; return CommonResult.success(userService.getById(userId)); }
这只是简单的处理全局异常,实际项目中会需要各种封装,参见Spring Boot项目优雅的全局异常处理方式
第三方注入Bean
@Bean
使用说明
(1)@Bean注解相当于spring的xml配置文件<bean>标签,告诉容器注入一个bean。
(2)@Bean 注解作用在方法上
(3)@Bean 指示一个方法返回一个 Spring 容器管理的 Bean
(4)@Bean 方法名与返回类名一致,首字母小写
(5)@Bean 一般和 @Component 或者 @Configuration 一起使用
(6)@Bean 注解默认作用域为单例 singleton 作用域,可通过 @Scope(“prototype”) 设置为原型作用域
Bean 名称
(1)默认情况下 Bean 名称就是方法名,比如下面 Bean 名称便是 myBean:
@Bean
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}(2)@Bean 注解支持设置别名。比如下面除了主名称 myBean 外,还有个别名 myBean1(两个都可以使用)
@Bean("myBean1")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}(3)@Bean 注解可以接受一个 String 数组设置多个别名。比如下面除了主名称 myBean 外,还有别名 myBean1、myBean2(三个都可以使用)
@Bean({"myBean1", "myBean2"})
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}@Bean 与其他注解一起使用
(1)@Bean 注解常常与 @Scope、@Lazy,@DependsOn 和 @link Primary 注解一起使用:
@Profile 注解:为在不同环境下使用不同的配置提供了支持,如开发环境和生产环境的数据库配置是不同的
@Scope 注解:将 Bean 的作用域从单例改变为指定的作用域
@Lazy 注解:只有在默认单例作用域的情况下才有实际效果
@DependsOn 注解:表示在当前 Bean 创建之前需要先创建特定的其他 Bean
(2)比如下面样例,Bean 的作用域默认是单例的,我们配合 @Scope 注解将其改成 prototype 原型模式(每次获取 Bean 的时候会有一个新的实例)
@Bean()
@Scope("prototype")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}Bean 初始化和销毁时调用相应的方法
(1)实际开发中,经常会遇到在 Bean 使用之前或使用之后做些必要的操作,Spring 对 Bean 的生命周期的操作提供了支持:我们可以通过 @Bean 注解的 initMethod 和 destrodMethod 进行指定 Bean 在初始化和销毁时需要调用相应的方法。
(2)下面是一个简单的样例:
public class MyBean {
public void init() {
System.out.println("MyBean开始初始化...");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyBean销毁...");
}
public String get() {
return "MyBean使用...";
}
}
@Bean(initMethod="init", destroyMethod="destroy")
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}@Configuration
使用说明
(1)@Configuration注解底层是含有@Component ,所以@Configuration 具有和 @Component 的作用。
(2)@Configuration注解相当于spring的xml配置文件中<beans>标签,里面可以配置bean。
Demo
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyConfigration {
@Bean
public String hello() {
return "welcome to hangge.com";
}
}import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
String hello;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
return hello;
}
}@Qualifier
当有多个同一类型的bean时,使用@Autowired导入会报错,提示当前对象并不是唯一,Spring不知道导入哪个依赖,这个时候,我们可以使用@Qualifier进行更细粒度的控制,选择其中一个候选者,一般于@Autowired搭配使用,示例如下:
@Autowired
@Qualifier("deptService")
private DeptService deptService;@Scope
用于生命一个spring bean的作用域,作用的范围一共有以下几种:
- singleton:唯一 bean 实例,Spring 中的 bean 默认都是单例的。
- prototype:每次请求都会创建一个新的 bean 实例,对象多例。
- request:每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP request 内有效。
- session:每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效。
/**
* 单例对象
*/
@RestController
@Scope("singleton")
public class HelloController {
}启动类相关
@PropertySource
这个注解是用来读取我们自定义的配置文件的,比如导入test.properties和bussiness.properties两个配置文件,用法如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@PropertySource(value = {"test.properties","bussiness.properties"})
public class PropertyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PropertyApplication.class, args);
}
}@ImportResource
用来加载 xml 配置文件,比如导入自定义的aaa.xml文件,用法如下:
@ImportResource(locations = "classpath:aaa.xml")
@SpringBootApplication
public class PropertyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PropertyApplication.class, args);
}
}


