目录:
- WebSocket简介
- WebSocket和Http的区别
- Springboot整合WebSocket
- WebSocket在Spring中的多例模式
- 一些部署问题
参考/来源:
WebSocket简介
产生的原因
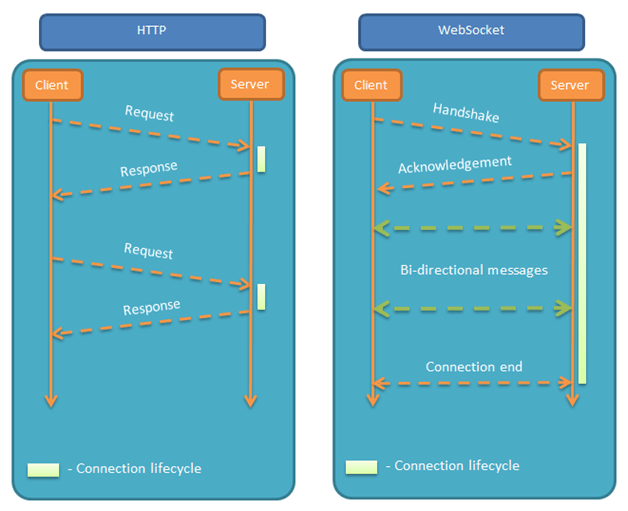
初次接触 WebSocket 的人,都会问同样的问题:我们已经有了 HTTP 协议,为什么还需要另一个协议?它能带来什么好处?
答案很简单,因为 HTTP 协议有一个缺陷:通信只能由客户端发起。
举例来说,我们想了解今天的天气,只能是客户端向服务器发出请求,服务器返回查询结果。HTTP 协议做不到服务器主动向客户端推送信息。
这种单向请求的特点,注定了如果服务器有连续的状态变化,客户端要获知就非常麻烦。我们只能使用“轮询”:每隔一段时候,就发出一个询问,了解服务器有没有新的信息。最典型的场景就是聊天室。
轮询的效率低,非常浪费资源(因为必须不停连接,或者 HTTP 连接始终打开)。因此,工程师们一直在思考,有没有更好的方法。WebSocket 就是这样发明的。
概念
WebSocket 协议在2008年诞生,2011年成为国际标准。所有浏览器都已经支持了,是HTML5的一个新特性。
它的最大特点就是,服务器可以主动向客户端推送信息,客户端也可以主动向服务器发送信息,是真正的双向平等对话,属于服务器推送技术的一种。
其他特点包括:
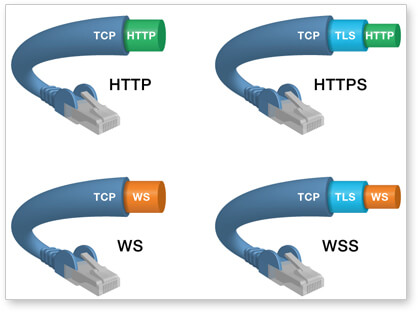
(1)建立在 TCP 协议之上,服务器端的实现比较容易。
(2)与 HTTP 协议有着良好的兼容性。默认端口也是80和443,并且握手阶段采用 HTTP 协议,因此握手时不容易屏蔽,能通过各种 HTTP 代理服务器。
(3)数据格式比较轻量,性能开销小,通信高效。
(4)可以发送文本,也可以发送二进制数据。
(5)没有同源限制,客户端可以与任意服务器通信。
(6)协议标识符是ws(如果加密,则为wss),服务器网址就是 URL。
ws://example.com:80/some/path
WebSocket和Http的对比
相同点
- 都是基于TCP的应用层协议。
- 都使用Request/Response模型进行连接的建立。
- 在连接的建立过程中对错误的处理方式相同,在这个阶段WS可能返回和HTTP相同的返回码。
- 都可以在网络中传输数据。
不同点
- WS使用HTTP来建立连接,但是定义了一系列新的header域,这些域在HTTP中并不会使用。
- WS的连接不能通过中间人来转发,它必须是一个直接连接。
- WS连接建立之后,通信双方都可以在任何时刻向另一方发送数据。
- WS连接建立之后,数据的传输使用帧来传递,不再需要Request消息。
- WS的数据帧有序。
Springboot整合WebSocket
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
/**
* 开启WebSocket支持
* @author zhengkai.blog.csdn.net
*/
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
WebSocketServer实现
因为WebSocket是类似客户端服务端的形式(采用ws协议),那么这里的WebSocketServer其实就相当于一个ws协议的Controller
直接@ServerEndpoint(“/imserver/{userId}”) 、@Component启用即可,然后在里面实现@OnOpen开启连接,@onClose关闭连接,@onMessage接收消息等方法。
新建一个ConcurrentHashMap webSocketMap 用于接收当前userId的WebSocket,方便IM之间对userId进行推送消息。单机版实现到这里就可以。
集群版(多个ws节点)还需要借助mysql或者redis等进行处理,改造对应的sendMessage方法即可。
package com.softdev.system.demo.config;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.websocket.OnClose;
import javax.websocket.OnError;
import javax.websocket.OnMessage;
import javax.websocket.OnOpen;
import javax.websocket.Session;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import cn.hutool.log.Log;
import cn.hutool.log.LogFactory;
/**
* @author zhengkai.blog.csdn.net
*/
@ServerEndpoint("/imserver/{userId}")
@Component
public class WebSocketServer {
static Log log=LogFactory.get(WebSocketServer.class);
/**静态变量,用来记录当前在线连接数。应该把它设计成线程安全的。*/
private static int onlineCount = 0;
/**concurrent包的线程安全Set,用来存放每个客户端对应的MyWebSocket对象。*/
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String,WebSocketServer> webSocketMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据*/
private Session session;
/**接收userId*/
private String userId="";
/**
* 连接建立成功调用的方法*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session,@PathParam("userId") String userId) {
this.session = session;
this.userId=userId;
if(webSocketMap.containsKey(userId)){
webSocketMap.remove(userId);
webSocketMap.put(userId,this);
//加入set中
}else{
webSocketMap.put(userId,this);
//加入set中
addOnlineCount();
//在线数加1
}
log.info("用户连接:"+userId+",当前在线人数为:" + getOnlineCount());
try {
sendMessage("连接成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("用户:"+userId+",网络异常!!!!!!");
}
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
if(webSocketMap.containsKey(userId)){
webSocketMap.remove(userId);
//从set中删除
subOnlineCount();
}
log.info("用户退出:"+userId+",当前在线人数为:" + getOnlineCount());
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
*
* @param message 客户端发送过来的消息*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) {
log.info("用户消息:"+userId+",报文:"+message);
//可以群发消息
//消息保存到数据库、redis
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(message)){
try {
//解析发送的报文
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(message);
//追加发送人(防止串改)
jsonObject.put("fromUserId",this.userId);
String toUserId=jsonObject.getString("toUserId");
//传送给对应toUserId用户的websocket
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(toUserId)&&webSocketMap.containsKey(toUserId)){
webSocketMap.get(toUserId).sendMessage(jsonObject.toJSONString());
}else{
log.error("请求的userId:"+toUserId+"不在该服务器上");
//否则不在这个服务器上,发送到mysql或者redis
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param session
* @param error
*/
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
log.error("用户错误:"+this.userId+",原因:"+error.getMessage());
error.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 实现服务器主动推送
*/
public void sendMessage(String message) throws IOException {
this.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
}
/**
* 发送自定义消息
* */
public static void sendInfo(String message,@PathParam("userId") String userId) throws IOException {
log.info("发送消息到:"+userId+",报文:"+message);
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(userId)&&webSocketMap.containsKey(userId)){
webSocketMap.get(userId).sendMessage(message);
}else{
log.error("用户"+userId+",不在线!");
}
}
public static synchronized int getOnlineCount() {
return onlineCount;
}
public static synchronized void addOnlineCount() {
WebSocketServer.onlineCount++;
}
public static synchronized void subOnlineCount() {
WebSocketServer.onlineCount--;
}
}
服务端消息推送
import com.softdev.system.demo.config.WebSocketServer;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* WebSocketController
* @author zhengkai.blog.csdn.net
*/
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("index")
public ResponseEntity<String> index(){
return ResponseEntity.ok("请求成功");
}
@GetMapping("page")
public ModelAndView page(){
return new ModelAndView("websocket");
}
@RequestMapping("/push/{toUserId}")
public ResponseEntity<String> pushToWeb(String message, @PathVariable String toUserId) throws IOException {
WebSocketServer.sendInfo(message,toUserId);
return ResponseEntity.ok("MSG SEND SUCCESS");
}
}客户端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>websocket通讯</title>
</head>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js"></script>
<script>
var socket;
function openSocket() {
if(typeof(WebSocket) == "undefined") {
console.log("您的浏览器不支持WebSocket");
}else{
console.log("您的浏览器支持WebSocket");
//实现化WebSocket对象,指定要连接的服务器地址与端口 建立连接
//等同于socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8888/xxxx/im/25");
//var socketUrl="${request.contextPath}/im/"+$("#userId").val();
var socketUrl="http://localhost:9999/demo/imserver/"+$("#userId").val();
socketUrl=socketUrl.replace("https","ws").replace("http","ws");
console.log(socketUrl);
if(socket!=null){
socket.close();
socket=null;
}
socket = new WebSocket(socketUrl);
//打开事件
socket.onopen = function() {
console.log("websocket已打开");
//socket.send("这是来自客户端的消息" + location.href + new Date());
};
//获得消息事件
socket.onmessage = function(msg) {
console.log(msg.data);
//发现消息进入 开始处理前端触发逻辑
};
//关闭事件
socket.onclose = function() {
console.log("websocket已关闭");
};
//发生了错误事件
socket.onerror = function() {
console.log("websocket发生了错误");
}
}
}
function sendMessage() {
if(typeof(WebSocket) == "undefined") {
console.log("您的浏览器不支持WebSocket");
}else {
console.log("您的浏览器支持WebSocket");
console.log('{"toUserId":"'+$("#toUserId").val()+'","contentText":"'+$("#contentText").val()+'"}');
socket.send('{"toUserId":"'+$("#toUserId").val()+'","contentText":"'+$("#contentText").val()+'"}');
}
}
</script>
<body>
<p>【userId】:<div><input id="userId" name="userId" type="text" value="10"></div>
<p>【toUserId】:<div><input id="toUserId" name="toUserId" type="text" value="20"></div>
<p>【toUserId】:<div><input id="contentText" name="contentText" type="text" value="hello websocket"></div>
<p>【操作】:<div><a onclick="openSocket()">开启socket</a></div>
<p>【操作】:<div><a onclick="sendMessage()">发送消息</a></div>
</body>
</html>WebSocket在Spring中的多例模式
单例与多例冲突
如果在WebSocket的回调方法中调用Spring的其他Bean,比如调用Dao层:
MapMapper mapMapper = ApplicationContextRegister.getApplicationContext().getBean(MapMapper.class);
mapMapper.updateAllBranchVisible();正常我们开发SpringBoot,都是借助Spring容器的IOC的特性,将Service、Dao等直接依赖注入,类似于下面。
@Autowired
private MapMapper mapMapper;但是这么写会报错,在执行 mapMapper.updateAllBranchVisible(); 方法时报空指针,即MapMapper的Bean没有注入进来。
所以可以通过Spring容器上下文,用工厂类的方式创建MapMapper的Bean。
@Component
public class ApplicationContextRegister implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext curApplicationContext) {
applicationContext = curApplicationContext;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
}原理
要弄懂原因,首先要了解Spring注入Bean的方式:
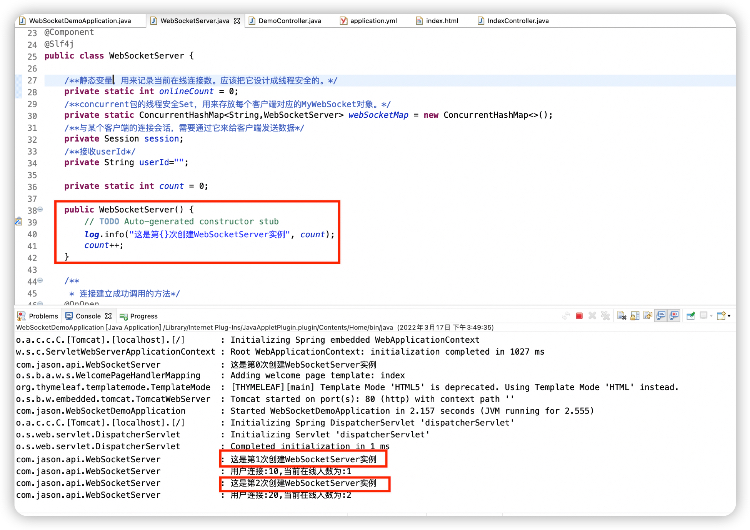
有些人可能不知道,Spring默认实例化的Bean是单例模式,这就意味着在Spring容器加载时,就注入了MapMapper的实例,不管再调用多少次接口,加载的都是这个Bean同一个实例。
而WebSocket是多例模式,websocket每有一个连接就会创建一个对象。
在项目启动时第一次初始化实例时,MapMapper的实例的确可以加载成功,但可惜这时WebSocket是无用户连接的。当有第一个用户连接时,WebSocket类会创建第二个实例,但由于Spring的Dao层是单例模式,所以这时MapMapper对应的实例为空。后续每连接一个新的用户,都会再创建新的WebSocket实例,当然MapMapper的实例都为空。
一些部署问题
ServerEndpointExporter错误
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name ‘serverEndpointExporter’ defined in class path resource [com/xxx/WebSocketConfig.class]: Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer not available
如果tomcat部署一直报这个错,请移除 WebSocketConfig 中@Bean ServerEndpointExporter 的注入 。
ServerEndpointExporter 是由Spring官方提供的标准实现,用于扫描ServerEndpointConfig配置类和@ServerEndpoint注解实例。使用规则也很简单:
如果使用默认的嵌入式容器 比如Tomcat 则必须手工在上下文提供ServerEndpointExporter。
如果使用外部容器部署war包,则不需要提供提供ServerEndpointExporter,因为此时SpringBoot默认将扫描服务端的行为交给外部容器处理,所以线上部署的时候要把WebSocketConfig中这段注入bean的代码注掉。



