目录:
- 简介
- Spring AOP
- 缓存声明
- 缓存配置
- 集成caffeine
- 高级使用
参考/来源:
简介
Spring Cache不是一个具体的缓存实现方案,而是一个对缓存使用的抽象(Cache Abstraction)。
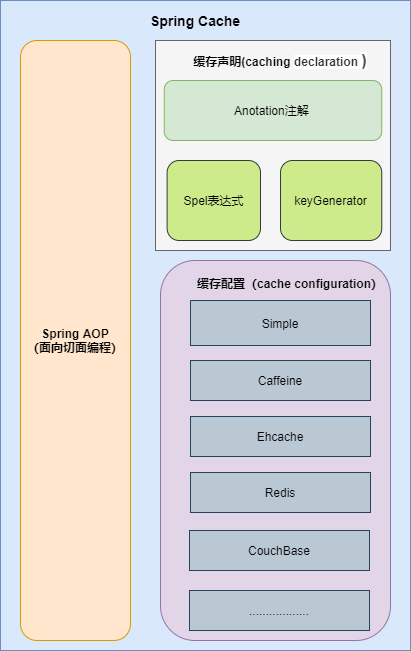
Spring AOP
代理类在方法调用前可以获取方法的参数,当调用方法结束后,可以获取调用该方法的返回值,通过这种方式就可以实现缓存的逻辑。
缓存声明
缓存声明,也就是标识需要缓存的方法以及缓存策略。
Spring Cache 提供了五个注解。
- @Cacheable:根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,下次同样的参数来执行该方法时可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而不需要再次执行该方法;
- @CachePut:根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用;
- @CacheEvict:根据一定的条件删除缓存;
- @Caching:组合多个缓存注解;
- @CacheConfig:类级别共享缓存相关的公共配置。
@Cacheable注解
@Cacheble注解表示这个方法有了缓存的功能。
@Cacheable(value="user_cache",key="#userId", unless="#result == null")
public User getUserById(Long userId) {
User user = userMapper.getUserById(userId);
return user;
}上面的代码片段里,getUserById方法和缓存user_cache 关联起来,若方法返回的User对象不为空,则缓存起来。第二次相同参数userId调用该方法的时候,直接从缓存中获取数据,并返回。
缓存键Key
通常情况下,@Cacheable有一个属性key可以直接定义缓存key,开发者可以使用SpEL语言定义key值。
若没有指定属性key,缓存抽象提供了
KeyGenerator来生成key ,默认的生成器代码见下图: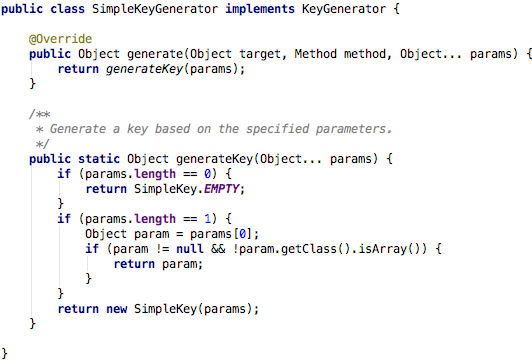
自定义Key生成方式时,可以实现
org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator接口,然后指定@Cacheable的keyGenerator属性.@Cacheable(value="user_cache", keyGenerator="myKeyGenerator", unless="#result == null") public User getUserById(Long userId) { //... }缓存条件
注解里可以通过
condition属性,通过Spel表达式返回的结果是true 还是false 判断是否需要缓存。@Cacheable(cacheNames="book", condition="#name.length() < 32") public Book findBook(String name){}除了condition,
unless属性也可以决定结果是否缓存,不过是在执行方法后。@Cacheable(value="user_cache",key="#userId", unless="#result == null") public User getUserById(Long userId) { }上面的代码片段里,当返回的结果为null则不缓存。
@CachePut注解
@CachePut注解作用于缓存需要被更新的场景,和 @Cacheable 非常相似,但被注解的方法每次都会被执行。
返回值是否会放入缓存,依赖于condition和unless,默认情况下结果会存储到缓存。
@CachePut(value = "user_cache", key="#user.id", unless = "#result != null")
public User updateUser(User user) {
userMapper.updateUser(user);
return user;
}当调用updateUser方法时,每次方法都会被执行,但是因为unless属性每次都是true,所以并没有将结果缓存。当去掉unless属性,则结果会被缓存。
@CacheEvict注解
@CacheEvict 注解的方法在调用时会从缓存中移除已存储的数据。
@CacheEvict(value = "user_cache", key = "#id")
public void deleteUserById(Long id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
}当调用deleteUserById方法完成后,缓存key等于参数id的缓存会被删除,而且方法的返回的类型是Void ,这和@Cacheable明显不同。
缓存配置
Spring Cache是一个对缓存使用的抽象,它提供了多种存储集成。
要使用它们,需要简单地声明一个适当的CacheManager :一个控制和管理Cache的实体。
以caffeine本地内存缓存演示如何集成。
集成caffeine
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.29</version>
</dependency>配置文件
server:
port: 80
spring:
datasource :
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username : root
password : qianhao123
driver-class-name : com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
配置类
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public Caffeine caffeineConfig() {
return Caffeine.newBuilder().maximumSize(10000). // 标识本地缓存的最大数量是10000条
expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.MINUTES); // 每个缓存数据在写入60分钟后失效
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(Caffeine caffeine) {
CaffeineCacheManager caffeineCacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
caffeineCacheManager.setCaffeine(caffeine);
return caffeineCacheManager;
}
}实体类
public class UserEntity {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return id + " " + username + " " + password;
}
}mapper层
@Mapper
public interface UserMapping {
@Select("select * from user")
public List<UserEntity> getAll();
}接口
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapping userMapping;
/**
* 查看所有用户
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Cacheable(value = "user_cache", unless = "#result == null")
public String user() {
return userMapping.getAll().toString();
}
}启动
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCacheForCaffineApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCacheForCaffineApplication.class, args);
}
}启动后,第一次访问接口,会打印sql到控制台,第二次访问就不会打印,说明访问成功。
高级使用
Spring Cache的功能很强大,设计也非常优雅。特别适合缓存控制没有那么细致的场景。比如门户首页,偏静态展示页面,榜单等等。这些场景的特点是对数据实时性没有那么严格的要求,只需要将数据源缓存下来,过期之后自动刷新即可。这些场景下,Spring Cache就是神器,能大幅度提升研发效率。
但在高并发大数据量的场景下,精细的缓存颗粒度的控制上,还是需要做功能扩展。
- 多级缓存;
- 列表缓存;
- 缓存变更监听器



